JDBC使得我们可以通过java代码访问数据库。
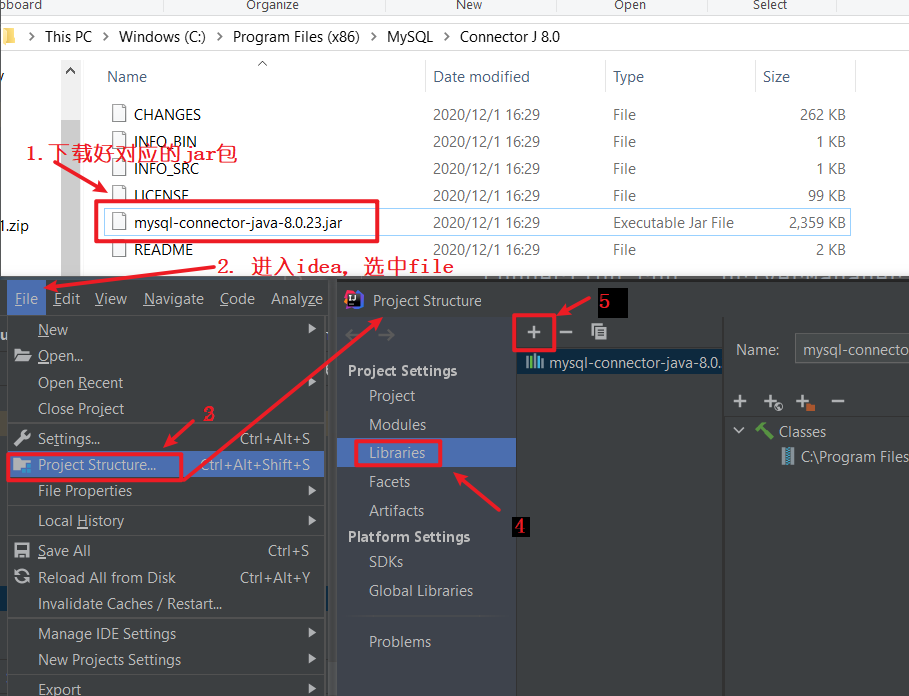
1 将mysql-connector jar包载入到当前项目中
2 使用java代码连接到数据库 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 String name = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" ;PreparedStatement psta = null ;Connection con = null ; try { Class c = Class.forName(name); con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" , "root" , "" ); String sql = "update mydata" + " set username = ?" + " where username = ?" ; psta = con.prepareStatement("" ); psta.setString(1 ,"changed" ); psta.setString(2 ,"4" ); ResultSet rs = psta.executeQuery(); int re = psta.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(re); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (psta!=null ) { try { psta.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } if (con!=null ){ try { con.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } }
预编译的好处是提高代码的可读性、安全性,并且因为sql代码是预编译的,所以性能得到了提升。
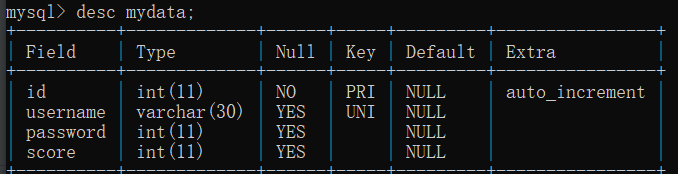
3 修改、删除和插入 要对表进行操作,首先要知道表的结构,比如查询mydata表,先查看它的结构
对表进行修改,要用executeUpdate()执行sql语句。
【插入】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 PreparedStatement psta = con.prepareStatement("insert into mydata values(?,?,?,?)" ); psta.setInt(1 ,id); psta.setString(2 ,username); psta.setInt(3 ,password); psta.setInt(4 ,score); int r = psta.executeUpdate();if (r>0 ){ System.out.println("sql success!" ); } else { System.out.println("sql failed" ); }
【修改】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 PreparedStatement psta = con.prepareStatement("update mydata set username='newName' where username=?" );psta.setString(1 ,username); int r = psta.executeUpdate();if (r>0 ){ System.out.println("sql success!" ); } else { System.out.println("sql failed" ); }
【删除】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 PreparedStatement psta = con.prepareStatement("delete from data where username=?" ); psta.setString(1 ,username); int r = psta.executeUpdate();if (r>0 ){ System.out.println("sql success!" ); } else { System.out.println("sql failed" ); }
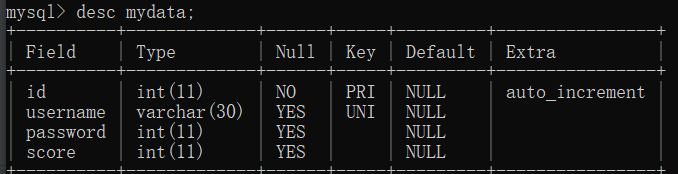
4 查询 要做查询,首先要知道表的结构,比如查询mydata表,先查看它的结构
对表进行查询,要用executeQuery()执行sql语句。
然后写查询语句,因为查询的结果一般有多条,所以用ResultSet接收查询结果
1 ResultSet rs = psta.executeQuery();
注意这里调用的方法是executeQuery,而不是executeUpdate。
用变量接收查询结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 while (rs.next()){ int id = rs.getInt(1 ); String username = rs.getString(2 ); int password = rs.getInt(3 ); int score = rs.getInt(4 ); }
5 事务控制 假如要执行很多条sql命令,多数情况下,如果其中某一条命令执行失败,那么其他命令的执行就没有意义了,这时想让数据表恢复到所有这一批sql命令执行之前的状态,就要通过事务来完成。将一批sql命令定义为一个事务,事务中只要有sql语句执行失败,数据库就会回滚到事务开始时的状态,只有事务中的sql命令全部执行成功后才会将事务(即其中的所有sql命令)全部提交。
其原理就是在事务开始前,存储引擎先对事务涉及到的表内容做一个记录备份,如果需要回滚,就将备份覆盖到受影响的字段;不需要回滚,就将备份删除。
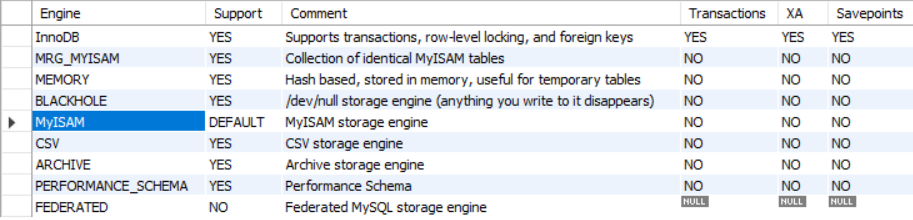
5.1 修改mysql默认引擎 通过show engines; 查看当前mysql服务器支持的引擎
可以看到默认引擎是MyISAM,它不支持事务操作(也不支持外键)。所以想要进行事务操作,要先将默认引擎改为InnoDB(支持事务,且默认将每一条sql语句视为一个完整事务,执行con.setAutoCommit(false);命令可改为手动提交事务)。
innodb速度没有myisam快
在my.ini文件中,修改default-storage-engine=MYISAM 即可更换默认引擎(修改完后记得重启mysql服务器)
因为之前的表是在myisam引擎下创建的,因此要对旧表的引擎做一个更新(更换引擎后新创建的表不用),执行:alter table mydata engine=innodb;
5.2 通过JDBC提交事务 获取到连接con后
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 con.setAutoCommit(false ); PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement;try { psta = con.prepareStatement("delete from mydata where username=?" ); psta.setString(1 ,"tom" ); psta.executeUpdate(); psta = con.prepareStatement("delete from mydatda where username=?" ); psta.setString(1 ,"lisa" ); psta.executeUpdate(); con.commit(); } catch (SQLException e){ e.printStackTrace(); con.rollback(); }
6 DAO封装 Database Access Object(DAO)封装了针对某一张数据表的操作(增删改查),这样之后要对某张表进行操作,直接通过DAO进行即可,为开发提供了方便。
【规范】
DAO类名称:表名+Dao。比如Emp表的DAO叫EmpDao
DAO所属包名称:公司域名.dao,比如com.google.dao
【DAO类示例——user_info表的dao】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 public class User_infoDao { public int add (String username, String password) { int re = 0 ; String sql = "insert into user_info (username, password, from_date) values (?,?,?)" ; java.sql.Date date = new java .sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); try { PreparedStatement ps = MyTool.createPreStatement(sql); ps.setString(1 ,username); ps.setString(2 ,password); ps.setDate(3 ,date); re = ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { MyTool.close(); } return re; } public int delete (String username) { int re = 0 ; String sql = "delete from user_info where username=?" ; try { PreparedStatement ps = MyTool.createPreStatement(sql); ps.setString(1 , username); re = ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { MyTool.close(); } return re; } public int delete (int id) { int re = 0 ; String sql = "delete from user_info where uid=?" ; try { PreparedStatement ps = MyTool.createPreStatement(sql); ps.setInt(1 , id); re = ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { MyTool.close(); } return re; } public int update (int uid, String username, String password) { int re = 0 ; String sql = "update user_info set " + "username=?, " + "password=? where uid=?" ; try { PreparedStatement ps = MyTool.createPreStatement(sql); ps.setString(1 , username); ps.setString(2 ,password); ps.setInt(3 ,uid); re = ps.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { MyTool.close(); } return re; } public ResultSet findAll () { ResultSet rs = null ; String sql = "select * from user_info" ; try { PreparedStatement ps = MyTool.createPreStatement(sql); rs = ps.executeQuery(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { MyTool.close(rs); } return rs; } }
7 实体类 实体类描述了某一张数据表的结构,它的作用就是存放JDBC查询结果的数据,一个实体类的实例就代表JDBC查询结果的一行,一个实体类数组可以用来存放一整个ResultSet。
【规范】
先创建实体类包,名称叫entity,与Dao包是并列关系。
在包内定义各个表的实体类,以下表为例
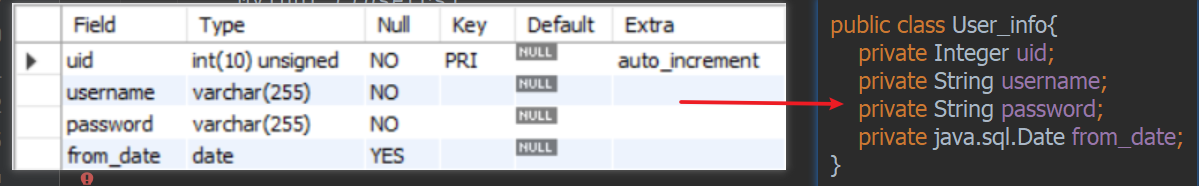
实体类名与数据表名一致。本例为user_info,实体类名为User_info
实体类的属性与数据表字段一致
实现了实体类后,可以对DAO封装的查询方法进行改进,这样后续调用DAO的方法时就完全不用与数据库相关的方法或者类进行交互了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public ArrayList<User_info> findAll () { ResultSet rs = null ; ArrayList<User_info> allUser = new ArrayList <>(); String sql = "select * from user_info" ; try { PreparedStatement ps = MyTool.createPreStatement(sql); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()){ int uid = rs.getInt(1 ); String username = rs.getString(2 ); String password = rs.getString(3 ); java.sql.Date date = rs.getDate(4 ); User_info tmp = new User_info (uid,username,password,date); allUser.add(tmp); } } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } finally { MyTool.close(rs); } return allUser; }